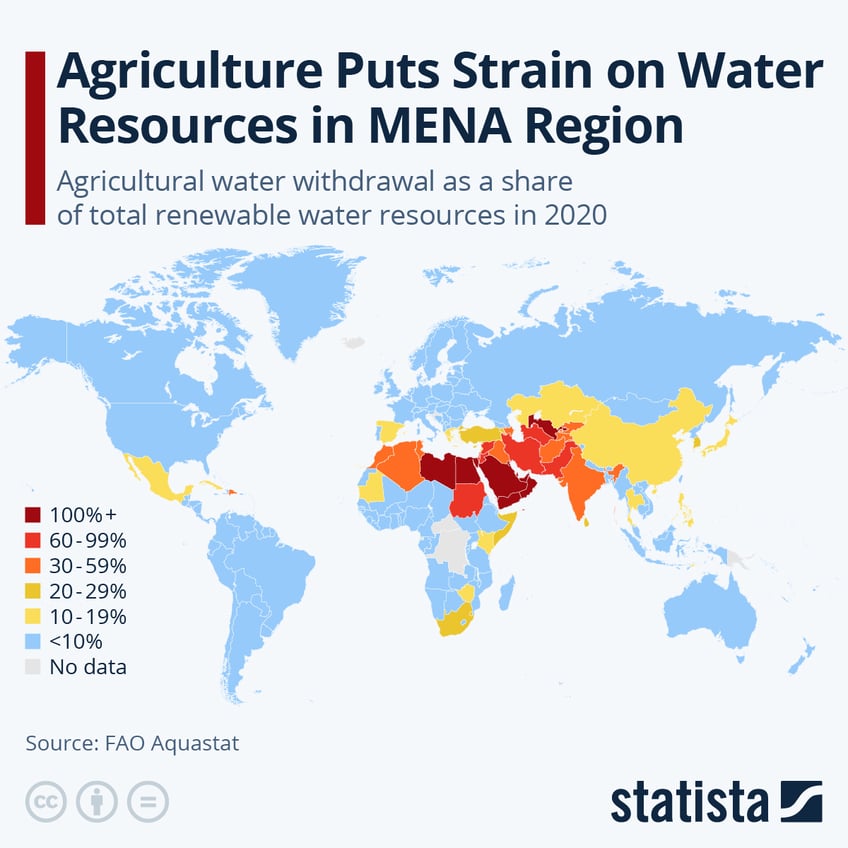
Agricultural water withdrawal way beyond the limit of renewable freshwater resources is most common today in countries in the Middle East and North Africa.
Statista's Katharina Buchholz reports that, according to the FAO Aquastat database where the latest available year for the data is 2020, several other nations, with Spain, South Africa, South Korea, Pakistan and India all sticking out for using up a higher share of their freshwater resources in agriculture than their neighbors.
You will find more infographics at Statista
Desert climates like on the Arabian peninsular make countries there overextend their annual water budgets by agriculture alone.
This has led to studies concluding that the United Arab Emirates, for example, could run out of groundwater by 2030. In Pakistan and Iran, between 63 and 70 percent of renewable freshwater resources were dedicated to agriculture in 2020, rising to 68 and 77 percent including all freshwater uses. Extensive and water-intensive agriculture, including cotton crops, is also driving up freshwater use in the semi-arid climates of Central Asia. Here, Uzbekistan used 111 percent of renewable water resources per year, followed by Turkmenistan at 65 percent (106 percent when counting all freshwater use). The only other country extending its freshwater budget only when combining agriculture and other freshwater uses was Jordan.
Agriculture accounts for 72 percent of all freshwater withdrawals globally, including a lot of overuse. According to the FAO, global freshwater resources per person have declined by 20 percent in the past decades, while water availability and quality have also deteriorated. Additional factors playing a role in this are pollution and climate change, stretching the precious resource even thinner.
October 16 marks World Food Day, which this year has the motto: Water is life, water is food. Leave no one behind.