The European Space Agency has also advocated for a unified time system for the moon
NASA welcomes its newest astronauts
Ten U.S. and 2 United Arab Emirate astronauts have just completed 2 years of training
- The White House has ordered NASA and other U.S. agencies to develop a new timekeeping system for the moon.
- The initiative aims to address the discrepancy in time perception caused by the moon's gravity, where time moves slightly faster compared to Earth.
- Kevin Coggins, NASA's top communications and navigation official, voiced the importance of tailoring timekeeping systems for celestial bodies.
NASA wants to come up with an out-of-this-world way to keep track of time, putting the moon on its own souped-up clock.
It's not quite a time zone like those on Earth, but an entire frame of time reference for the moon. Because there's less gravity on the moon, time there moves a tad quicker — 58.7 microseconds every day — compared to Earth. So the White House Tuesday instructed NASA and other U.S agencies to work with international agencies to come up with a new moon-centric time reference system.
"An atomic clock on the moon will tick at a different rate than a clock on Earth," said Kevin Coggins, NASA's top communications and navigation official. "It makes sense that when you go to another body, like the moon or Mars that each one gets its own heartbeat."
EARTH'S CHANGING SPIN MAY CAUSE TIMEKEEPERS TO SUBTRACT A SECOND FROM WORLD CLOCKS
So everything on the moon will operate on the speeded-up moon time, Coggins said.
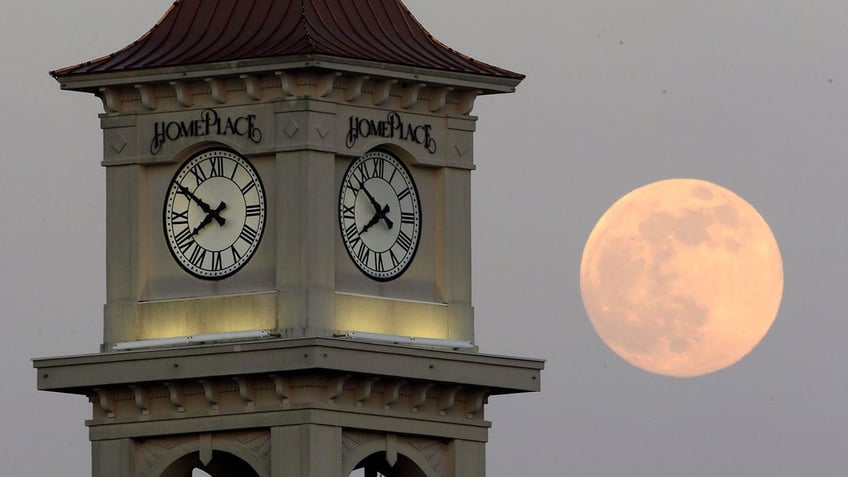
The moon rises behind the Home Place clock tower on June 22, 2013, in Prattville, Alabama. NASA has been ordered to come up with an out-of-this-world way to keep track of time, putting the moon on its own souped-up clock. (AP Photo/Dave Martin, File)
The last time NASA sent astronauts to the moon they wore watches, but timing wasn't as precise and critical as it now with GPS, satellites and intricate computer and communications systems, he said. Those microseconds matter when high tech systems interact, he said.
Last year, the European Space Agency said Earth needs to come up with a unified time for the moon, where a day lasts 29.5 Earth days.
The International Space Station, being in low Earth orbit, will continue to use coordinated universal time or UTC. But just where the new space time kicks in is something that NASA has to figure out. Even Earth's time speeds up and slows down, requiring leap seconds.
Unlike on Earth, the moon will not have daylight saving time, Coggins said.
The White House wants NASA to come up with a preliminary idea by the end of the year and have a final plan by the end of 2026.
NASA is aiming to send astronauts around the moon in September 2025 and land people there a year later.
