Youngsters have been especially impacted by mpox outbreaks raging in Africa, with children under five accounting for nearly a third of the cases in Burundi, the UN children’s agency said Friday.
Burundi is the second hardest-hit country on the continent after the Democratic Republic of Congo.
“Children in Burundi are bearing the brunt of the mpox outbreak, with alarming rates of infection and severe health impacts,” said Paul Ngwakum, UNICEF’s Regional Health Advisor for Eastern and Southern Africa.
Ngwakum said two-thirds of cases in Burundi concerned people aged 19 and under.
“Of particular concern is the rise of mpox among children under five years of age, representing 30 percent of the reported cases,” he told reporters in Geneva, speaking via videolink from Bujumbura.
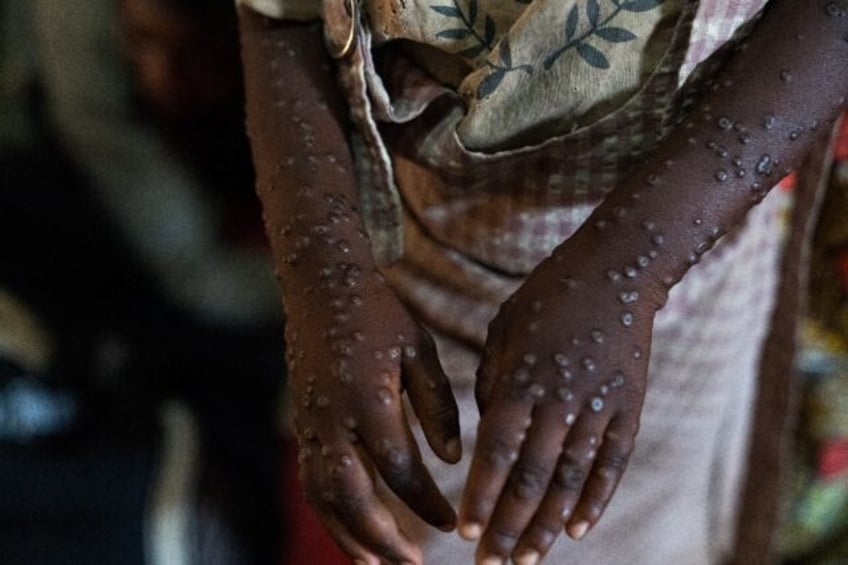
Mpox, previously known as monkeypox, is caused by a virus transmitted to humans by infected animals but can also be passed from human to human through close physical contact.
It causes fever, muscular aches and large boil-like skin lesions, and can in some cases be deadly.
The World Health Organization declared an international emergency last month, concerned by the surge in cases of the new clade 1b strain in the DRC that spread to nearby countries.
A total of 25,093 suspected mpox cases and 723 deaths were reported across the continent between January and September 8, WHO said.
Of those, 21,835 suspected cases and 717 deaths were reported in the DRC, while 1,489 suspected cases and no deaths have been reported in neighbouring Burundi.
Vulnerable populations
Research is still under way to discover how clade 1b compares to the original strain.
The outbreak in DRC has proved deadlier than previous mpox epidemics but this could be because the vulnerable populations in the conflict-torn country are now being affected.
“It may indeed be that it’s in a population who simply cannot respond immunologically to yet another threat,” WHO spokeswoman Margaret Harris told reporters Friday.
While no deaths have been registered in Burundi yet, Ngwakum stressed that many children in the region were already weakened by low immunity and underlying illnesses and “will need critical treatment to be able to avoid them from dying”.
The last time WHO declared a global health emergency over mpox was in 2022 when the original mpox clade 2 that had long been endemic in central Africa suddenly began spreading around the world.
That outbreak mainly impacted gay and bisexual men with more than 100,000 cases reported and 222 deaths, according to the WHO.
‘Can be stopped’
Ngwakum said the geographical area where the virus is spreading in Burundi remains limited.
With swift action “we can limit the spread, contain the virus, and potentially end the outbreak with no lives lost,” he said.
I “think this can be stopped within a very few weeks.”
UNICEF, he said, was urgently appealing for nearly $59 million to scale up responses across six African countries, including Burundi.
Immunisation with vaccines originally developed for smallpox could help stem the spread.
WHO last week for the first time prequalified an mpox vaccine, the MVA-BN, and Ngwakum said UNICEF was working to procure doses for Burundi.
On Thursday, mpox vaccines were administered in Africa for the first time, with several hundred high-risk individuals receiving jabs in Rwanda.
The DRC has said it will begin its vaccination campaign on October 2.
