The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) V-safe website quietly stopped collecting adverse event reports with no reason or explanation.
The V-safe website simply states: “Thank you for your participation. Data collection for COVID-19 vaccines concluded on June 30, 2023.” If you go there today, V-safe directs users to the FDA’s VAERS website for adverse event reporting, even though officials continually derided VAERS as “passive” and “unverified.”
VAERS and V-safe are mutually exclusive safety collection databases operated by the FDA and CDC, respectively. VAERS is an older way of collecting safety data where one can fill out a form online, or manually, or by calling a toll-free number, whereas V-safe is a device “app” which requires online registration. Both VAERS and V-safe collect personal information, lot numbers, dates and associated information, but V-safe was an active collection system geared towards a younger app-using demographic.
Here is the last report before deletion.
Does this mean that the CDC believes that the mRNA Covid-19 injections are so safe, there is no need to monitor adverse event reports any longer? What is the argument against continued monitoring, especially since the V-safe website was already up and paid for?
While CDC’s V-safe was stealthily and abruptly turned off, refusing to accept new safety reports, to this very day the CDC continues to urge everyone ages 6 months and older to stay up to date with COVID-19 vaccines and boosters.
As a drug safety expert, I personally can’t cite another example of any agency or manufacturer halting collection of safety data. It seems even worse because mRNA technology is relatively new with long-term manifestations unknown. On top of this, both manufacturers and the FDA refuse to share the list of ingredients, such as lipid nanoparticles, which could affect individuals differently and take a long time to manifest clinically.
Safety Data Collection Should Never Stop
Now, contrast that with the fact that the National Highway Traffic and Safety Administration (NHTSA) will still accept a safety report for a 30-year-old Ford Bronco II. Indeed, this is an oddly specific example, but only because I drove this exact vehicle as a family hand-me-down as a student, through my residency, fellowship, for my tenure as a Yale professor on the mean streets of New Haven and even during my years at the FDA as a medical officer /senior medical analyst.
Like mRNA shots, Bronco IIs are still available on the market and people are still using them up to this very day. My Bronco became an intermittent topic of conversation with friends and FDA colleagues. One day, I was informed by a patrolling security guard at the FDA that it was the oldest car on campus.
I didn’t know much about cars (or mRNA technology) back then, but when a fellow FDA-er informed me that my Bronco II had noteworthy safety problems and that the NHTSA still had their eye on this vehicle (rollover accidents were more common and more fatal) I addressed the problem: I got rid of the reliable relic, even though I really liked it.
NHTSA is still accepting safety reports on things like my 30-year-old Ford Bronco II, but the CDC isn’t accepting new safety reports on 2-year old novel mRNA vaccines.
CDC No longer accepting safety reports despite rapidly increasing safety findings:
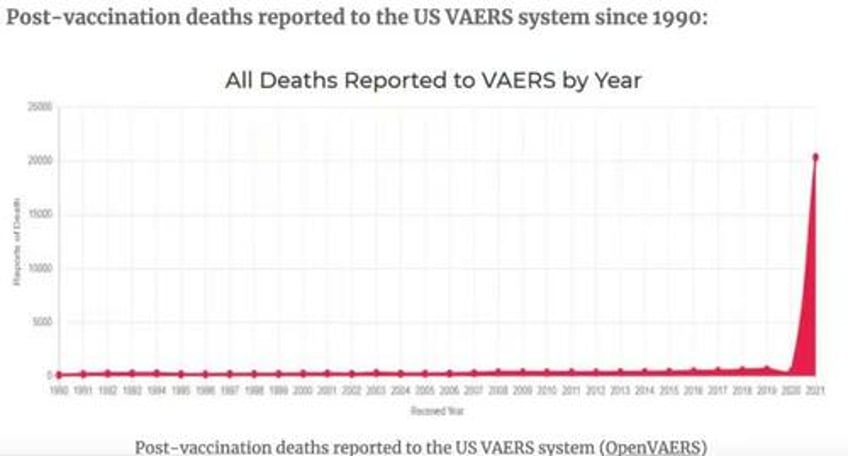
Unlike my old Bronco, mRNA injections have only been on the market for about two years, and according to the FDA Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) database, mRNA “vaccines” have been named the primary suspect in over 1.5 million adverse event reports, of which there are >20,000 heart attacks and >27,000 cases of myocarditis and pericarditis just in the USA alone. Worldwide numbers would be greater. According to many references, including an FDA-funded study out of Harvard, VAERS reports represent fewer than 1 percent of vaccine adverse events that actually occur.
Interestingly, the NHTSA link above on my Ford Bronco II only shows: one parts recall, one investigation and 23 complaints, and still features a button in the upper right hand corner for submitting new complaints.
Wikipedia defines an humanitarian crisis or humanitarian disaster as a: “singular event or a series of events that are threatening in terms of health, safety or well-being of a community or large group of people.” Based on VAERS and previous V-safe findings, adverse events from mRNA shots in the USA alone could be considered a humanitarian crisis.
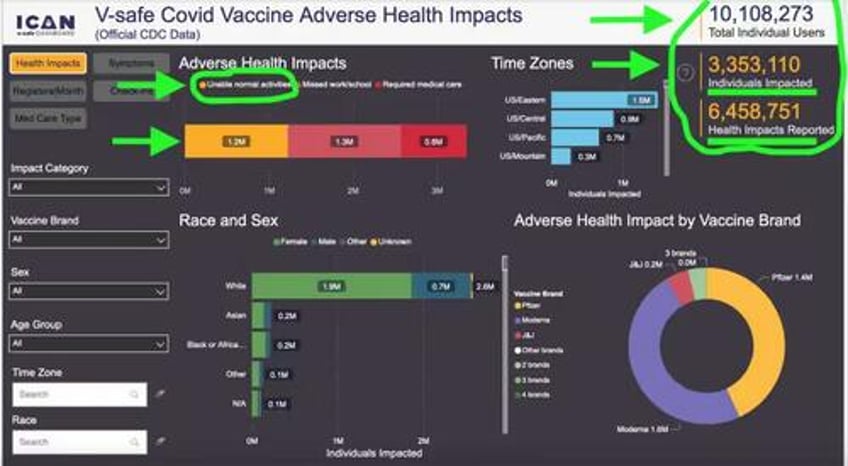
Despite those alarming clinical findings, the CDC has concluded that collecting new safety reports is somehow no longer in the interest of America’s public health. Existing data from the V-safe site showed around 6.5 million adverse events/health impacts out of 10.1 million users, with around 2 million of those people unable to conduct normal activities of daily living or needing medical care, according to a third-party rendering of its findings. In other words, despite mRNA shots still being widely available and the CDC promoting its continued use, it’s “case closed” with regards to collecting new safety reports, under today’s federal public health administration.
Will the CDC opine on the existing data or justify its halting of collecting new safety data? To the best of my knowledge, stopping the collection of public health information doesn’t have a clinical justification or scientific precedence — especially when it comes to an actively marketed product.
In George Orwell’s 1984, characters were told by The Party to “reject the evidence of your eyes and ears.” Now, the CDC isn’t even allowing that evidence to be collected for viewing (and prospective rejecting). It’s a terrible idea for any product, let alone novel mRNA technologies.
Dr. David Gortler, a 2023 Brownstone Fellow, is a pharmacologist, pharmacist, research scientist and a former member of the FDA Senior Executive Leadership Team who served as senior advisor to the FDA Commissioner on matters of: FDA regulatory affairs, drug safety and FDA science policy. He is a former Yale University and Georgetown University didactic professor of pharmacology and biotechnology, with over a decade of academic pedagogy and bench research, as part of his nearly two decades of experience in drug development. He also serves as a scholar at the Ethics and Public Policy Center