Mark Zuckerberg is back in the hot seat, this time facing explosive allegations that Meta deliberately swiped millions of books from notorious digital pirate sites LibGen and Anna's Archive to train its cutting-edge AI model, Llama 3.
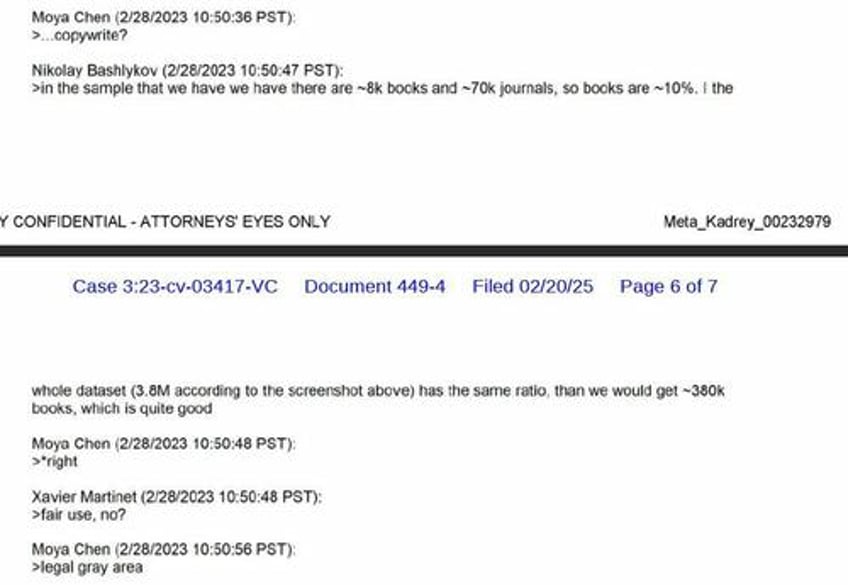
According to recently filed court documents, Meta executives were allegedly openly discussing their desperate need for high-quality content, acknowledging in a damning email, "Books are actually more important than web data." To that end, the company allegedly turned straight to piracy hubs stacked high with stolen literary treasures - without a second thought or a single cent paid to their rightful owners, according to Forbes.
Meta staff turned to LibGen, home to more than 7.5 million pirated books and 81 million stolen research papers, to fill that gap. They did the same with Anna’s Archive.
...
In recently filed court documents, Meta, led by founder and CEO Mark Zuckerberg, is alleged to have deliberately and explicitly authorized a raid on LibGen—and Anna's Archive, another massive digital pirate haven—to train its latest AI model, Llama 3.
The fallout has infuriated authors worldwide whose life's work may have been quietly scooped up and fed into Zuckerberg’s latest technological brainchild without credit, consent, or compensation.
As the article notes, Meta’s 2024 financial statements showcase revenues topping a staggering $164 billion, with profits nearing $62 billion. Clearly, Meta had the means and muscle to fairly compensate creators, publishers, and researchers. Instead, they allegedly chose to steal that content for training purposes.
Critics argue this saga is more than just corporate greed;
They might even have acted as the leader in LLM input data and created licensed arrangements that respected an author’s rights. Imagine if the company had the corporate culture to be a leader on one of society’s latest and most important questions: Who owns content in the LLM?
Coincidentally, Meta's "focus on long-term impact" core value states: "We emphasize long-term thinking that encourages us to extend the timeline for the impact we have, rather than optimizing for near-term wins."
It seems very clear that Meta was indeed optimizing for near-term wins in this case, instead of outlining a corporate culture and leadership position of collaboration and authenticity.
Meta’s defense, meanwhile, leans on the "fair use" argument - suggesting their AI transforms stolen content into something sufficiently new. But legal experts stress fair use typically applies to educators, reviewers, and critics - not trillion-dollar tech giants profiteering off mass commercial data harvesting.
The author of the Forbes piece checked The Atlantic's Alex Reisner’s LibGen tracking tool and made a disturbing discovery: all five of their own published books were found pirated and included in Meta’s dataset.
Why isn’t this criminal copyright infringement? https://t.co/hkZeYxlkJJ
— Cernovich (@Cernovich) March 31, 2025
A major class-action lawsuit has been filed alleging copyright infringement and unfair competition - while other firms "are likely guilty of similar sins," according to the author.
Ultimately, this saga goes beyond Meta alone. The entire AI industry’s insatiable thirst for data urgently needs clear ethical guardrails. Tech giants must form sustainable, fair partnerships with content creators or risk stifling creativity, undermining intellectual property rights, and eroding public trust.