The cost of an electric vehicle (EV) battery pack can vary depending on composition and chemistry.
In this graphic, Visual Capitalist's Bruno Venditti and Sabrina Lam use data from Benchmark Minerals Intelligence to showcase the different costs of battery cells on popular electric vehicles.
Size Matters
Some EV owners are taken by surprise when they discover the cost of replacing their batteries.
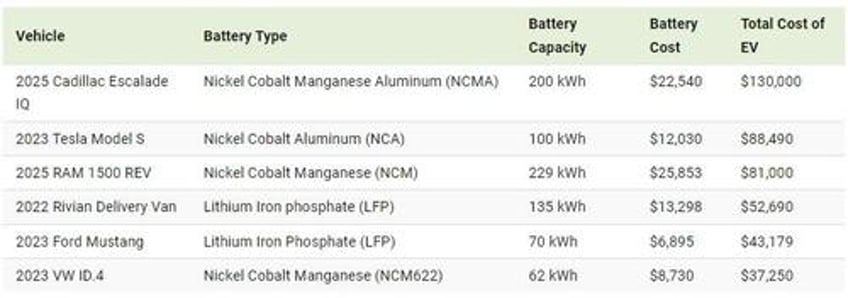
Depending on the brand and model of the vehicle, the cost of a new lithium-ion battery pack might be as high as $25,000:
The price of an EV battery pack can be shaped by various factors such as raw material costs, production expenses, packaging complexities, and supply chain stability. One of the main factors is chemical composition.
Graphite is the standard material used for the anodes in most lithium-ion batteries.
However, it is the mineral composition of the cathode that usually changes. It includes lithium and other minerals such as nickel, manganese, cobalt, or iron. This specific composition is pivotal in establishing the battery’s capacity, power, safety, lifespan, cost, and overall performance.
Lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (NCA) battery cells have an average price of $120.3 per kilowatt-hour (kWh), while lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide (NCM) has a slightly lower price point at $112.7 per kWh. Both contain significant nickel proportions, increasing the battery’s energy density and allowing for longer range.
At a lower cost are lithium iron phosphate (LFP) batteries, which are cheaper to make than cobalt and nickel-based variants. LFP battery cells have an average price of $98.5 per kWh. However, they offer less specific energy and are more suitable for standard- or short-range EVs.
Which Battery Dominates the EV Market?
In 2021, the battery market was dominated by NCM batteries, with 58% of the market share, followed by LFP and NCA, holding 21% each.
Looking ahead to 2026, the market share of LFP is predicted to nearly double, reaching 38%.
NCM is anticipated to constitute 45% of the market and NCA is expected to decline to 7%.