Nvidia has become an early winner of the generative AI boom.
The company reported record revenue in its second quarter earnings report, with sales of AI chips playing a large role. If we compare to other American competitors, what do the AI chip sales of Nvidia vs. AMD vs. Intel look like?
In the graphic below, Visual Capitalist's Jenna Ross and Sam Parker use earnings reports from each company to see their revenue over time.
A Clear Leader Emerges
While the companies don’t report revenue for their AI chips specifically, they do share revenue for their Data Center segment.
The Data Center segment includes chips like Central Processing Units (CPUs), Data Processing Units (DPUs), and Graphic Processing Units (GPUs). The latter are preferred for AI because they can perform many simple tasks simultaneously and efficiently.
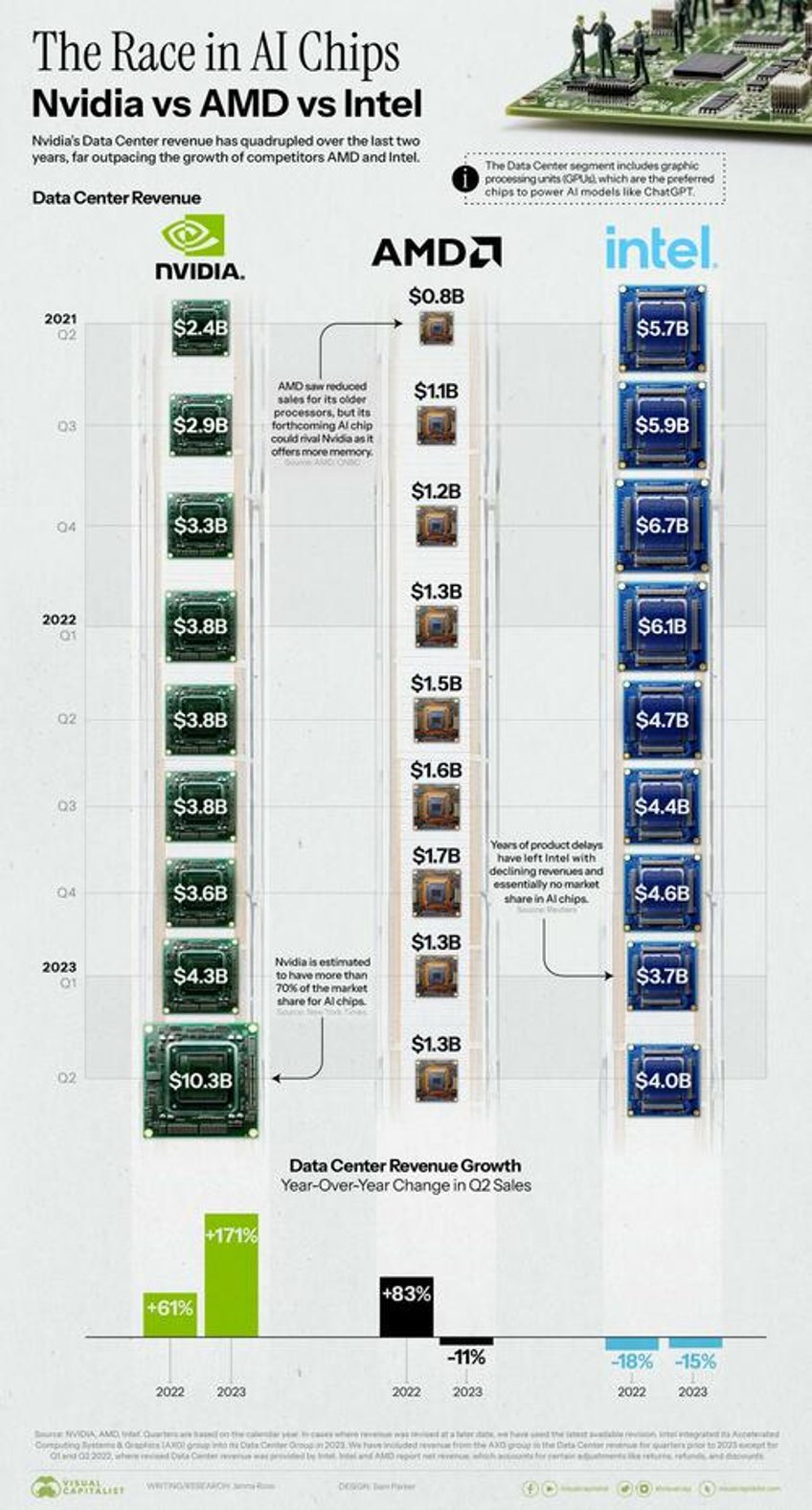
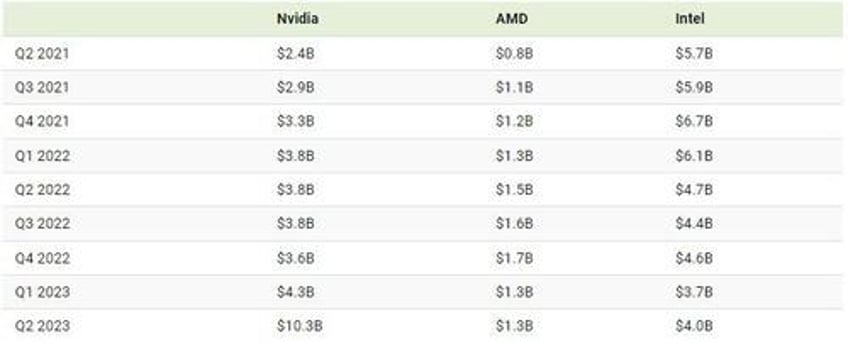
Below, we show how quarterly Data Center revenue has grown for Nvidia vs. AMD vs. Intel.
Source: Nvidia, AMD, Intel. Quarters are based on the calendar year. In cases where revenue was revised at a later date, we have used the latest available revision. Intel integrated its Accelerated Computing Systems & Graphics (AXG) group into its Data Center Group in 2023. We have included revenue from the AXG group in the Data Center revenue for quarters prior to 2023 except for Q1 and Q2 2022, where revised Data Center revenue was provided by Intel.
Nvidia’s Data Center revenue has quadrupled over the last two years, and it’s estimated to have more than 70% of the market share for AI chips.
The company achieved dominance by recognizing the AI trend early, becoming a one-stop shop offering chips, software, and access to specialized computers. After hitting a $1 trillion market cap earlier in 2023, the stock continues to soar.
Competition Between Nvidia vs. AMD vs. Intel
If we compare Nvidia vs. AMD, the latter company has seen slower growth and less revenue. Its MI250 chip was found to be 80% as fast as Nvidia’s A100 chip.
However, AMD has recently put a focus on AI, announcing a new MI300X chip with 192GB of memory compared to the 141GB that Nvidia’s new GH200 offers. More memory reduces the amount of GPUs needed, and could make AMD a stronger contender in the space.
In contrast, Intel has seen yearly revenue declines and has virtually no market share in AI chips. The company is better known for making traditional CPUs, and its foray into the AI space has been fraught with issues. Its Sapphire Rapids processor faced years of delays due to a complex design and numerous glitches.
Going forward, all three companies have indicated they plan to increase their AI offerings. It’s not hard to see why: ChatGPT reportedly runs on 10,000 Nvidia A100 chips, which would carry a total price tag of around $100 million dollars.
As more AI models are developed, the infrastructure that powers them will be a huge revenue opportunity.