During the regional bank failures in March, we directed our readership to focus on the next potential crisis: "CRE Nuke Goes Off With Small Banks Accounting For 70% Of Commercial Real Estate Loans." By late March, Morgan Stanley warned clients of an upcoming maturity wall in commercial real estate, which amounts to $500 billion of loans in 2024, and a total of $2.5 trillion in debt that comes due over the next five years.
In a recent Bloomberg interview, Barry Sternlicht's Starwood Capital Group warned that the CRE space is in a "Category 5 hurricane." He said, "It's sort of a blackout hovering over the entire industry until we get some relief or some understanding of what the Fed's going to do over the longer term."
The current downturn in CRE could persist for years, if not through the end of this decade. Jan Mischke, a partner at the McKinsey Global Institute, along with Olivia White, a senior partner at McKinsey, and Aditya Sanghvi, a senior partner and leader of McKinsey's real estate special initiative, published a note in Fortune, warning "$800 billion of office space in just nine cities could become obsolete by 2030."
The authors of the report blame the CRE downturn on the "shift to remote and hybrid work prompted two further shifts in people's behavior":
First, many residents, untethered from their offices and therefore less fearful of long commutes, moved away from urban cores. New York City's urban core (that is, the dozen densest counties in the metropolitan area) lost 5% of its population from mid-2020 to mid-2022. San Francisco's urban core (San Francisco County, Alameda County, and San Mateo County) lost 6%.
Second, consumers began shopping less at brick-and-mortar stores–and far less at stores in urban cores, where people were now less likely either to work or to live. Foot traffic near stores in metropolitan areas remains 10 to 20% below pre-pandemic levels, but the differences between urban and suburban traffic recovery are substantial. For example, in late 2022, foot traffic near New York's suburban stores was 16% lower than it had been in January 2020, while foot traffic near stores in the urban core was 36% lower.
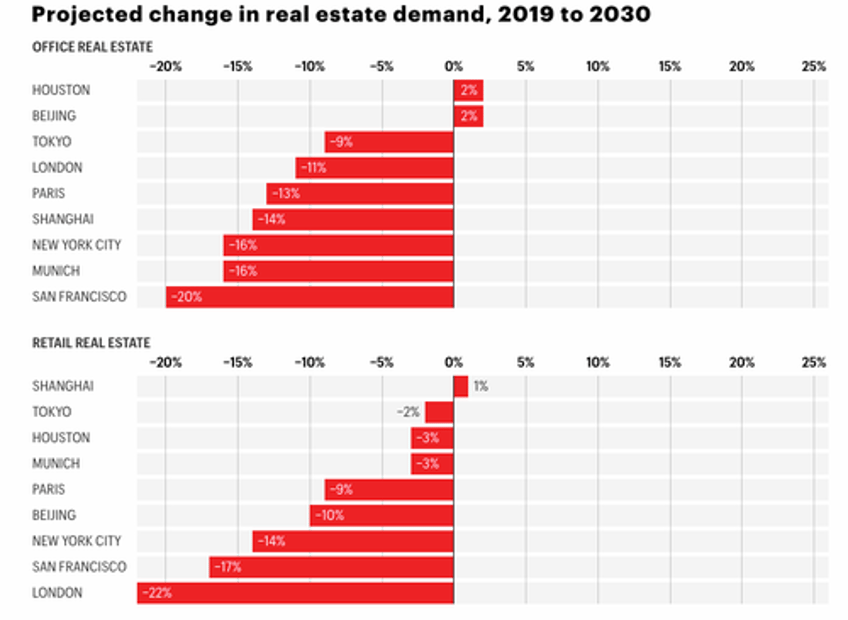
As fewer employees work in the office, demand for office space will fall. By 2030, such demand will be as much as 20% lower, depending on the city–even in a moderate scenario in which office attendance goes up but remains lower than it was before the pandemic.
And as fewer consumers shop at brick-and-mortar stores, demand for retail space will fall as well, according to our model. In the urban core of London, the hardest-hit city, demand for retail space will be 22% lower in 2030 than it was in 2019 in a moderate scenario.
Some of the most significant declines in office and retail space demand through 2030 will be in major US cities such as San Francisco and New York City.
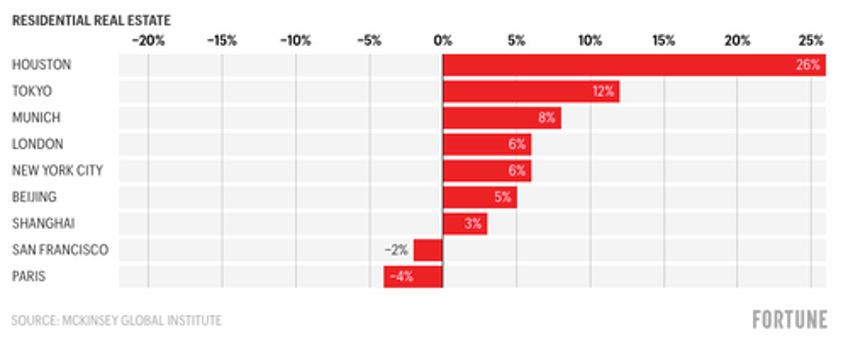
The authors note that the demand for "residential space will suffer less"... Well, according to their forecasting model.
"The reduced demand will have major impacts on urban stakeholders. For example, in just nine cities that we studied especially closely, $800 billion of office space could become obsolete by 2030. And macroeconomic complications could make matters even worse," the authors continued. Without office workers in downtown areas, economic recoveries in major cities will be a "U" shape or, in some cases, an "L."
The unraveling of downtowns is already underway. We shared a video this week of scenes of San Francisco's downtown transformed into a 'ghost town.' Building owners in the crime-ridden metro area are already giving up and defaulting as vacancies rise, crime surges, and refinancing is near impossible in today's climate as the Federal Reserve keeps interest rates sky-high to tame the worst inflation in a generation.
We shift our attention to Baltimore City, where office towers are being dumped in an apparent firesale.
- Beginning Of CRE Firesale? Baltimore Office Tower Dumped At 63% Discount
- CRE Panic Hits Baltimore As Second Office Tower Dumped At 69% Discount
The authors failed to report that the sliding demand for office towers isn't just because of "remote and hybrid work" but also due to an exodus of companies fleeing crime-ridden progressive cities that fail to enforce law and order.
If McKinsey's predictions are correct, certain segments of the CRE market are expected to experience prolonged turmoil for years. Some US mayors have proposed an immediate solution to convert office towers into multi-family units. However, this transformation could take years due to the time-consuming processes of obtaining permits and construction.