Previously enjoyed betting on the outcome of an event, like a Presidential election? The CFTC wants to make sure that doesn't happen again.
According to the Wall Street Journal, the regulator is now targeting "derivatives contracts based on political elections, athletic competitions and awards contests" to try and draw more prominent lines between investing and gambling.
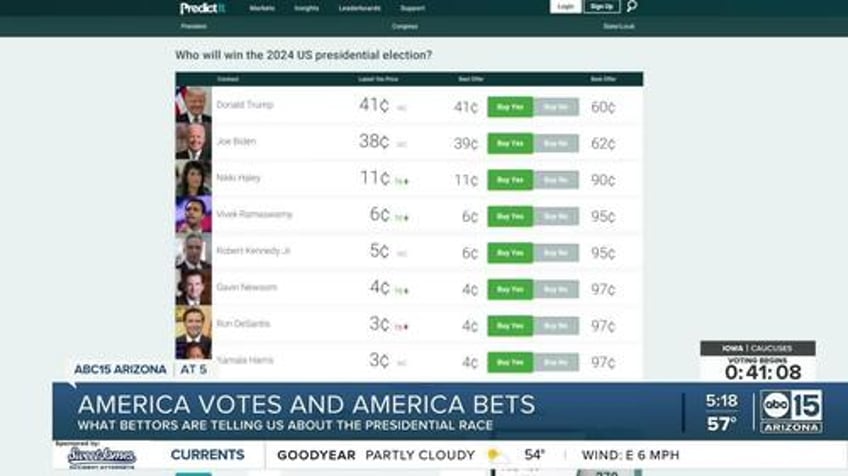
The Commodity Futures Trading Commission proposed a regulation to oversee event contracts, a rapidly growing market where investors bet on event outcomes, the report said.
The proposed regulation won’t affect sports betting through traditional sportsbooks regulated by state commissions or popular online platforms like DraftKings. Nor will it impact offshore platforms like Betfair, which currently allows U.S. election bets.
The proposal, approved 3-2 along party lines, will undergo public review before a final vote in the coming months. Democratic commissioners emphasized the potential threat to election integrity posed by political event contracts, particularly with a Biden-Trump rematch looming.
Christy Goldsmith Romero, a Democratic commissioner, said: “Never before has the sanctity of elections been so critical or so under threat. The CFTC should not allow products in our markets with an unacceptable risk of unchecked abuse and manipulation that could threaten the sanctity of elections, thereby threatening democracy and national security.”
Yet the proposal was called “grossly overbroad” by Summer Mersinger, a Republican commissioner, the report noted.
One company that offers "yes" or "no" betting questions has been Kalshi. Event contracts, though small compared to stocks or futures, have grown rapidly since Kalshi launched in 2021. Recent Kalshi contracts included wagers on whether "Oppenheimer" would win Best Picture and if Columbia University's president would be ousted.
CFTC Chair Rostin Behnam, a Democrat supporting the proposal, noted that more event contracts were listed in 2021 than in the previous 15 years combined.
The CFTC has previously blocked U.S. trading platforms from launching political betting markets. Last year, it prevented Kalshi from offering contracts based on which party controls Congress, prompting Kalshi to sue the agency in November over the rejection.
“We look forward to continuing to engage with our regulators and Congress, as we have always done, to ensure that our customers can participate in legitimate trading with legitimate use cases on a legitimate, regulated exchange and not on offshore and illegal markets where there is no customer protection or market integrity,” Mansour told WSJ.
CFTC regulations established after the 2010 Dodd-Frank Act prohibit event contracts involving terrorism, assassination, war, gaming, or illegal activities, but the lack of a clear definition of “gaming” led to disputes over whether it applies to sports and political contracts, prompting Friday's proposal to explicitly ban wagers on elections, sports, or awards contests.